Anatomy of the rectus abdominis muscles

By nature, the rectus abdominis muscles are located in the centre of the abdomen and consist of two parallel muscles extending from the ribs and reaching the pubic bone. These two parallel muscles are separated by a midline band of connective tissue called the "linea alba”.
What is diastasis recti?

Certain situations cause separation of the rectus abdominis muscles from the centre of the abdomen and stretching of the connective tissue (linea alba).
This situation is called diastasis recti or abdominal separation.
Who can develop this condition?

It occurs more frequently in pregnant women over the age of 35, in multiple pregnancies or when the baby is too big. Also, in newborns and, rarely, in men.
Newborns should be monitored frequently.
Pregnant women may develop abdominal separation due to intense stretching of the rectus abdominis during pregnancy. The problem is obvious after childbirth.
Clinical presentation

In the case of abdominal separation, the abdomen protrudes and is similar to a baby bump.
Abdominal separation is primarily an aesthetic problem. This is because the uterus, colon and small intestine as well as other organs within the abdomen are pushed outwards, as the abdominal muscles can no longer hold them together.
Diastasis recti, apart from being an aesthetic problem, can also cause back pain, constipation and urinary incontinence.
Sometimes it makes breathing and even moving around difficult.
Surgical treatment
 Treatment always requires surgery. It is almost always combined with abdominoplasty since women who have developed abdominal separation also suffer from significant skin sagging around the abdomen.
Treatment always requires surgery. It is almost always combined with abdominoplasty since women who have developed abdominal separation also suffer from significant skin sagging around the abdomen.
The rectus abdominis muscles are relocated at the midline with sutures. Placing a mesh is almost never necessary.
Sometimes herniation may also be present. The doctor will advise you to do an ultrasound for herniation diagnosis.
Difference between hernia and diastasis recti
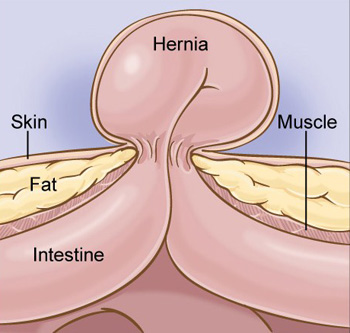
The diastasis recti is not an abdominal hernia nor is it life threatening.
In the case of a hernia, the abdominal organs push through the rectus abdominis muscles. In diastasis recti, there is no contact and the organs of the abdomen do not protrude beyond the rectus abdominis muscles.
Self-examination
Step 1: Lie on your back. Bend your knees and place the soles of your feet on the floor.
Step 2: Lift up your head
Step 3: Put your fingers in the middle of the abdomen. Move your fingertips to feel the gap between the abdominal muscles.
Photos of diastasis recti cases
https://www.keramidasevangelos.com/body/diastasis-of-the-rectus-abdominis-muscles#sigProId898eb42aeb
https://www.keramidasevangelos.com/body/diastasis-of-the-rectus-abdominis-muscles#sigProId415858341b
https://www.keramidasevangelos.com/body/diastasis-of-the-rectus-abdominis-muscles#sigProId681720e163
https://www.keramidasevangelos.com/body/diastasis-of-the-rectus-abdominis-muscles#sigProIdc26baa3528
https://www.keramidasevangelos.com/body/diastasis-of-the-rectus-abdominis-muscles#sigProId880164cfa7




 CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO
CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO
CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO
CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO
CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO
CAUTION! SURGERY VIDEO Send us your questions
Send us your questions






























Follow us

